在前端开发中,position: fixed是一个非常有用的CSS属性。简单来说,「position: fixed 会让元素脱离文档流,并且相对于浏览器的视口(viewport)进行定位。」 这意味着,不管你页面怎么滚动,这个元素都会固定在你设定的位置,比如右下角或者顶部。这种特性让它在实现固定导航栏、悬浮按钮或者广告位时非常有用。
不过,问题来了,如果我们的页面结构比较复杂,或者我们希望这个固定元素能相对于某个父元素进行定位,而不是整个浏览器窗口,该怎么办呢?下面让我们一起探究。
一、 搭建案例代码
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
APP
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
};
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
color: #2c3e50;
padding: 32px 20px;
width: calc(100vw - 64px);
height: calc(100vh - 40px);
}
</style>index.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<p v-for="i in 100" :key="i">
Container Content {{ i }}
</p>
<div class="footer">我是Container里面的footer</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {};
},
methods: {},
};
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.container {
background-color: aqua;
.footer {
position: fixed;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
background: rgb(138, 114, 114);
width: 100%;
border: 1px solid #9c9c9c;
color: white;
font-weight: bolder;
text-align: center;
padding: 30px 0;
}
}
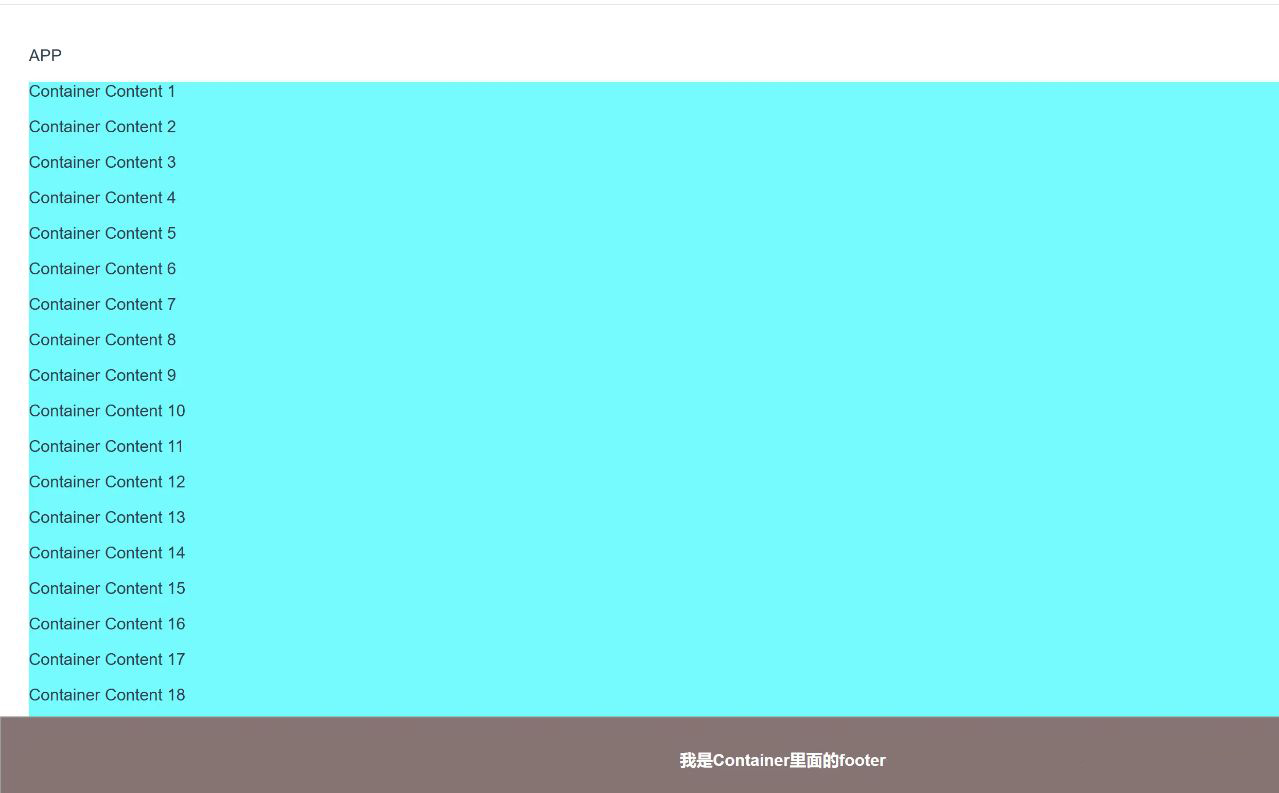
</style>效果
可以看到,从最内层到最外层的关系是APP组件 -> Container组件 -> footer组件,虽然「footer组件」是在「container组件」中,但是它还是相对于屏幕视口(viewport)的位置定位到了最底部。并且不受「APP组件」中内边距(padding: 32px 20px;)的限制。
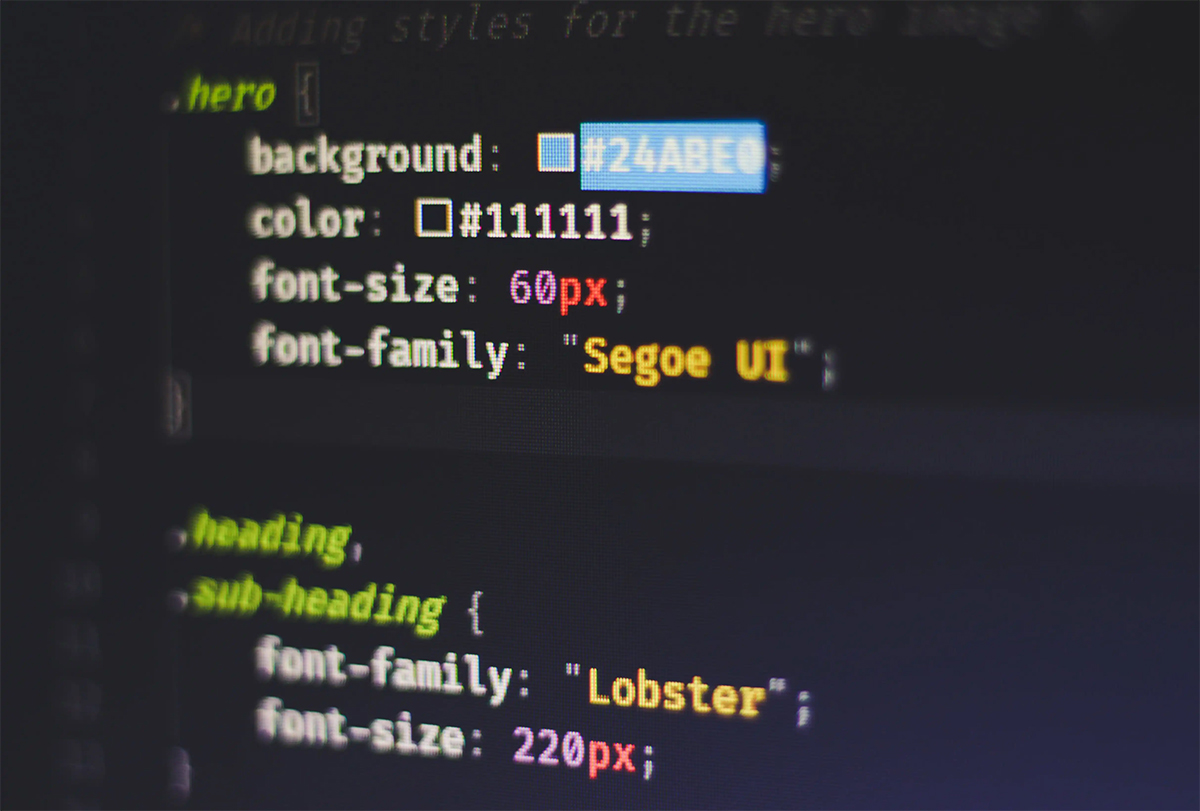
二、利用 transform 属性
CSS 的 transform 属性是一个非常强大的工具,它可以对元素进行平移、旋转、缩放等操作。而在这个场景中,它的另一个神奇作用是:如果一个元素设置了 transform 属性(除了 none),那么它的子元素中如果有 position: fixed,就会以这个设置了 transform 的元素为参照,而不是浏览器窗口。
// index.vue
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.container {
background-color: aqua;
transform: translate(0, 0); /* 关键属性 */
position: relative;
.footer {
position: fixed;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
background: rgb(138, 114, 114);
width: 100%;
border: 1px solid #9c9c9c;
color: white;
font-weight: bolder;
text-align: center;
padding: 30px 0;
}
}
</style>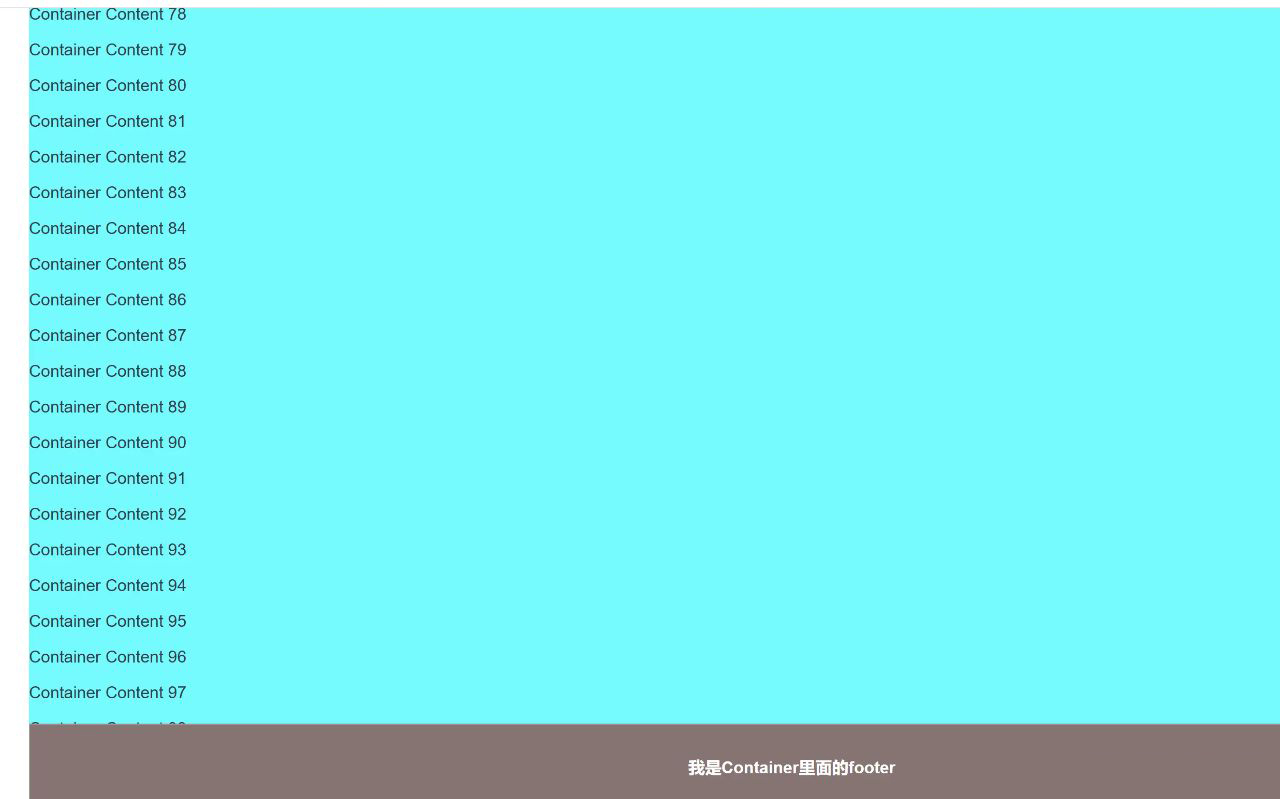
三、利用 perspective 属性
perspective 属性主要用于 3D 变换,它可以为元素创建一种“透视”效果。和 transform 类似,当一个元素设置了 perspective 属性时,它的子元素中的 position: fixed 也会以这个元素为参照。
// index.vue
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.container {
background-color: aqua;
perspective: 1000px; /* 关键属性 */
position: relative;
.footer {
position: fixed;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
background: rgb(138, 114, 114);
width: 100%;
border: 1px solid #9c9c9c;
color: white;
font-weight: bolder;
text-align: center;
padding: 30px 0;
}
}
</style>
四、利用 filter 属性(部分浏览器)
filter 属性可以对元素进行各种视觉效果的处理,比如模糊、对比度调整等。在某些浏览器中,如果一个元素设置了 filter 属性(除了 none),它的子元素中的 position: fixed 也会受到影响,以这个元素为参照。
「不过,这种方法的兼容性不太好,所以不太推荐在生产环境中使用。」
// index.vue
<style lang="scss" scoped>.
container {
background-color: aqua;
filter: brightness(1.2); /* 关键属性 */
position: relative;
.footer {
position: fixed;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
background: rgb(138, 114, 114);
width: 100%;
border: 1px solid #9c9c9c;
color: white;
font-weight: bolder;
text-align: center;
padding: 30px 0;
}
}
</style>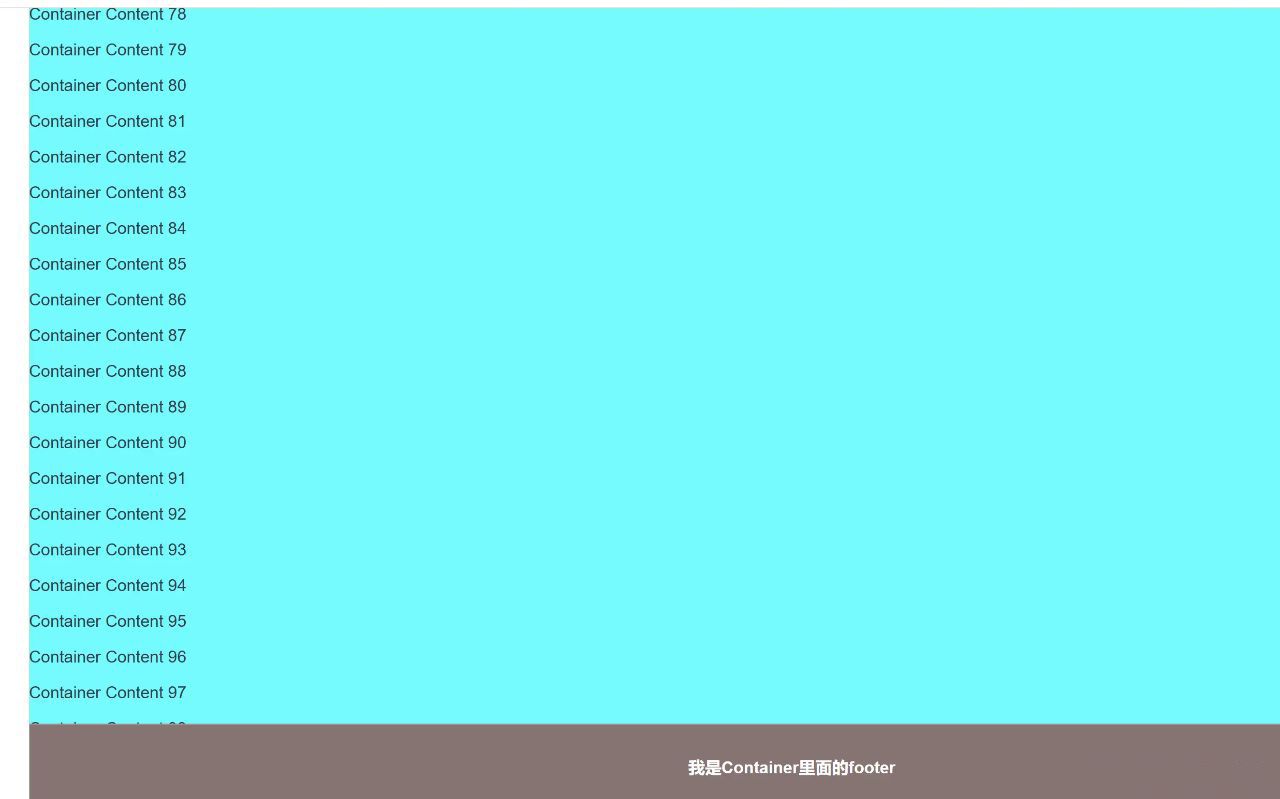
五、利用 backdrop-filter 属性
backdrop-filter 属性可以为元素背后的区域应用图形效果,如模糊、颜色调整等。它通常用于创建半透明背景下的视觉效果。
// index.vue
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.container {
background-color: aqua;
backdrop-filter: blur(10px); /* 关键属性 */
position: relative;
.footer {
position: fixed;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
background: rgb(138, 114, 114);
width: 100%;
border: 1px solid #9c9c9c;
color: white;
font-weight: bolder;
text-align: center;
padding: 30px 0;
}
}
</style>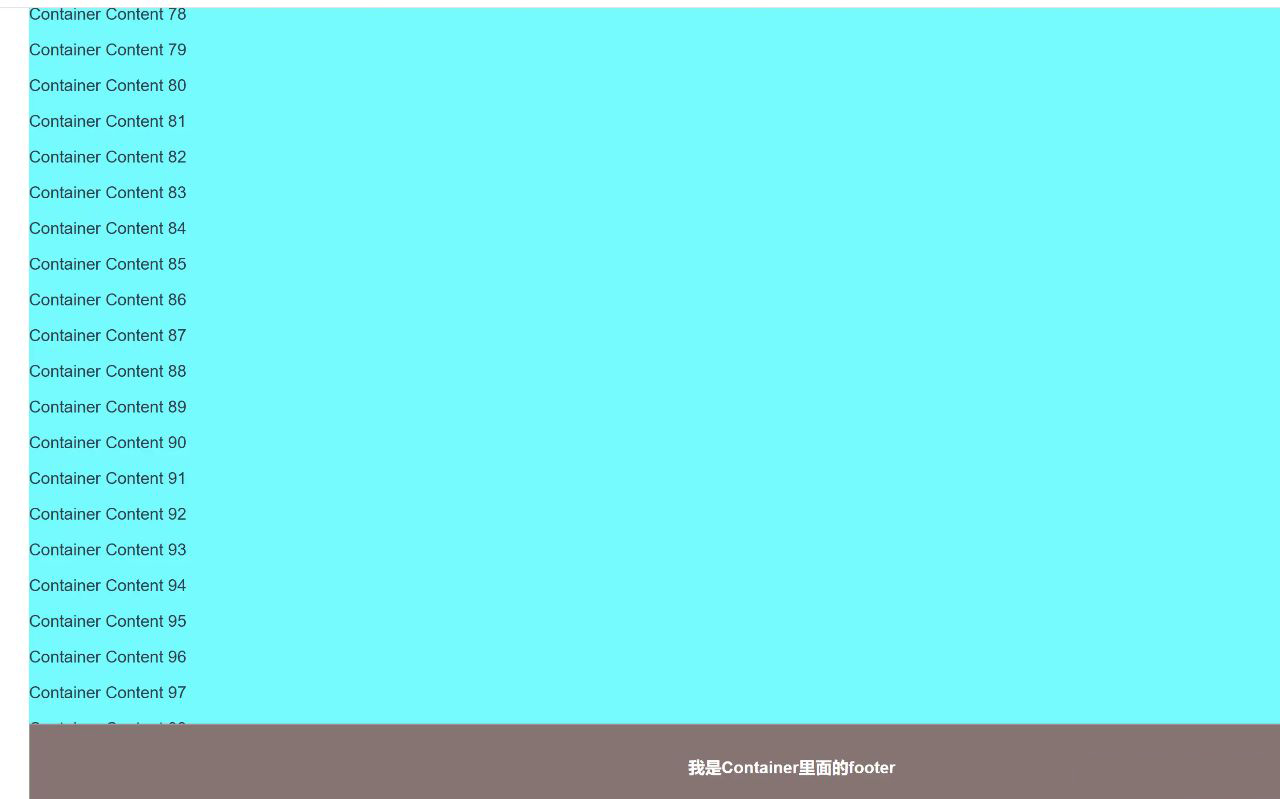
六、利用 contain: paint 属性
contain: paint 是 CSS 中的一个强大属性,用于优化页面的渲染性能。它通过限制元素的绘制范围,确保元素的内容只在自身的边界内绘制,而不会影响到外部的布局或内容。这种“绘制包含”可以减少浏览器的重绘和重排操作,从而提升页面性能
// index.vue
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.container {
background-color: aqua;
contain: paint; /* 关键属性 */
position: relative;
.footer {
position: fixed;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
background: rgb(138, 114, 114);
width: 100%;
border: 1px solid #9c9c9c;
color: white;
font-weight: bolder;
text-align: center;
padding: 30px 0;
}
}
</style>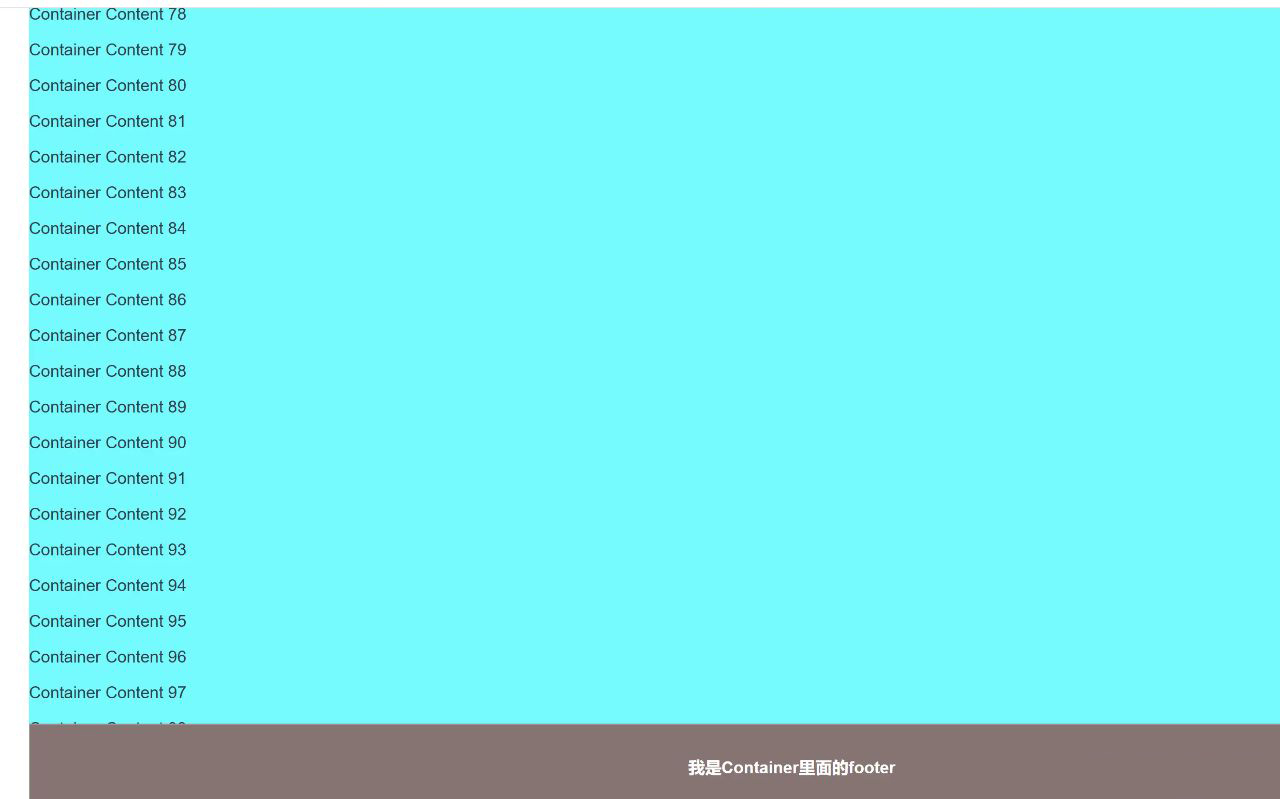
七、position:fixed 使用注意项
「布局影响:」 使用 position: fixed会将元素从正常的文档流中移除,这可能会影响到页面的布局。因此,在使用该属性时,需要确保其他元素不会因为被固定定位的元素而产生重叠或遮挡。「兼容性:」 虽然大多数现代浏览器都支持 position: fixed,但在一些旧版本的浏览器中可能存在兼容性问题。在使用此属性时,务必进行兼容性测试,以确保您的页面在各种浏览器中都能正确显示。「移动端适配:」 在移动端设备上,固定定位的元素可能会导致用户体验问题,特别是在滚动时可能会出现不可预料的行为。因此,在移动端使用 position: fixed时,需要特别注意,并进行相应的测试和调整。
八、原因
当父元素应用了 transform、filter backdrop-filter 等属性时,子元素的 position: fixed 会受到影响,原因如下:
「创建新的包含块」:根据 CSS 规范,当元素应用了 transform、filterbackdrop-filter(值不为none)时,该元素会创建一个新的包含块(containing block)。此时,其后代元素的position: fixed会相对于这个新的包含块进行定位,而不是相对于视口。「定位行为改变」:原本 position: fixed是相对于视口定位的,但当父元素有transform时,子元素的定位行为会“降级”为类似于position: absolute的效果
总结
总的来说,position: fixed是一个强大且灵活的CSS属性,可以帮助我们实现各种吸引人的页面效果。它能够让元素始终相对于浏览器视口固定位置,从而实现诸如导航栏、悬浮按钮等常见功能。然而,position: fixed 默认以浏览器视口为参照,这在某些复杂布局中可能不够灵活。幸运的是,通过一些巧妙的 CSS 技巧,我们可以改变 position: fixed 的相对参照值,使其能够以特定的父元素为基准。